Understanding the Most Frequently Encountered 3D Printing Problems
From its origins to its current uses, it has a rich history that is worth examining 3d printing troubleshooting: 15 most common problems & solutions.3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to aerospace. However, like any technology, it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding the most frequently encountered 3D printing problems is crucial for achieving successful prints consistently.
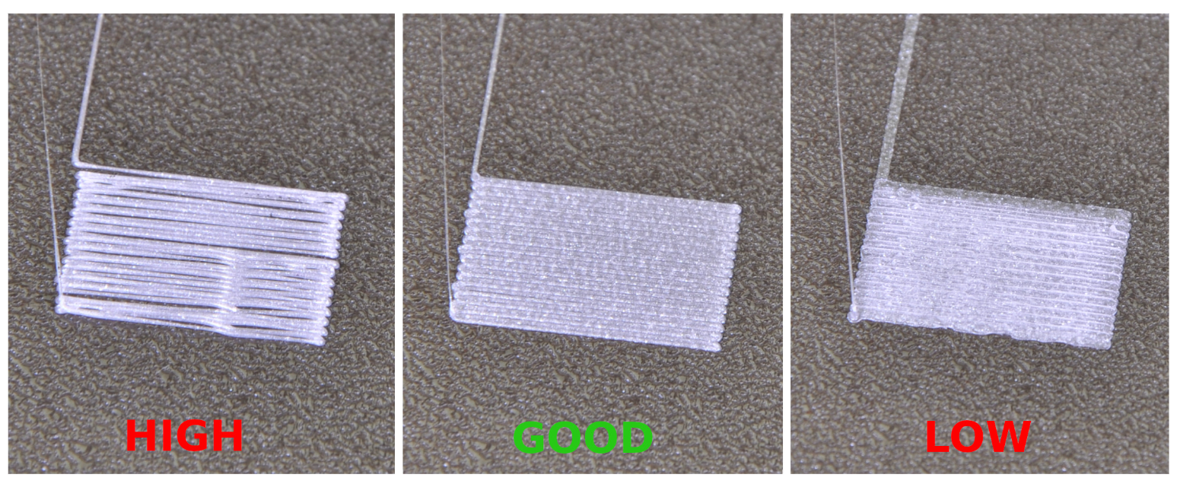
Calibrating the 3D Printer
One of the most common issues in 3D printing is related to calibration. Incorrect calibration can lead to poor adhesion, layer separation, and misshapen prints. To overcome this, it's essential to regularly calibrate the printer's build plate, nozzle height, and extruder steps. Additionally, ensuring the print bed is level and using the appropriate temperature for the filament can significantly improve print quality.
Dealing with Filament Jams and Clogs
Another frequent obstacle in 3D printing is filament jams and clogs. This occurs when the filament gets stuck in the extruder or nozzle, disrupting the printing process. To address this issue, regularly clean the extruder and nozzle, use high-quality filament, and ensure the filament is loaded correctly. Additionally, adjusting the printing temperature and reducing the printing speed can help prevent filament-related problems.
Overcoming Warping and Cracking
Warping and cracking of prints, especially with ABS and other high-temperature filaments, are common challenges in 3D printing. To combat this, utilizing a heated build plate, enclosing the printer to maintain a consistent temperature, and applying a suitable adhesive to the print bed can minimize warping and cracking. Furthermore, optimizing the cooling settings for the specific filament being used can also contribute to reducing these issues.
Resolving Layer Misalignment and Inconsistencies
Layer misalignment and inconsistencies can result in a lack of structural integrity and surface finish issues in 3D prints. To address this, ensuring the printer's belts and pulleys are properly tensioned, lubricating the moving parts, and checking for any obstructions in the print head's path are essential. Additionally, adjusting the printing speed and optimizing the slicing settings can help achieve more uniform and accurate prints.
By understanding and effectively addressing these common 3D printing problems, enthusiasts and professionals alike can enhance their printing experience and produce high-quality, reliable prints consistently. Embracing a proactive approach to troubleshooting and implementing the appropriate solutions is key to unlocking the full potential of 3D printing technology.




